
When trying to choose the correct product for your livestock there are a number of factors to take into account to ensure you get optimal coverage for the right price all while reducing the risk of resistance on your farm. Our guide to parasite control should give you all the information you need to make the right choice for you.
What kind of wormer should I use?
Wormers are used to treat and control parasitic infections from roundworm, lungworm, tapeworms and liver fluke. These wormers (or Anthelmintics) can be categorised into the following groups.
Group 1: Benzimidazoles (BZ)
Group 2: Levamisole (Imidazothiazoles) (LV)
Group 3: Macrocyclic lactones, including avermactins and milbemycins (ML)
Group 4: Amino acetonitrile derivatives (Monepantel) (AD)
Group 5: Spiroindoles (SI)
Wormers in these groups are effective against all the major species or roundworm and lungworm, with some also being effective against liver fluke and tapeworms. Wormers from Group 3 (ML) both injectables and pour ons are effective against ectoparasites.
| Parasite | Information | Products |
| Gutworms | Worming is a necessity when trying to break the cycle of gutworms especially where cattle are grazing in infected areas. Treatment should aim to reduce the disease and minimise contamination of the pasture. Symptoms of gutworm can include diarrhoea, decreased appetite and loss of weight. Gutworm can cause severe damage to the stomach and small intestine which will cause parasitic gastroenteritis, this will not only negatively affect the health of the animal but will affect the profitability for the farmer. |
Macrocyclic Lactone (ML), Benzimidazoles (BZ) and Levamisole (LV) products are most commonly used in the treatment of gutworm. |
| Lungworms | Lungworm infection usually occurs in younger livestock in the later stages of the grazing season. Without adequate lungworm control cattle can me more susceptible to pneumonia. Symptoms of lungworm can include a short, sharp cough that becomes worse with exercise, in severe cases the animal will have obvious difficulty breathing. Lungworm infections cause a high susceptibility to respiratory viruses and bacteria. Infected cattle are prone to contracting severe bronchial pneumonia which if left untreated can lead to death. |
Macrocyclic Lactone (ML), Benzimidazoles (BZ) and Levamisole (LV) products are most commonly used in the treatment of lungworm. |
| Liver Fluke |
There are many factors to take into account when treating for liver fluke in cattle. In particular you should take into account the risk, the time of year and the stage of development of the fluke. You should always seek advice from a vet or responsible seller. If rumen fluke is suspected you should discuss your options with your vet as treatment is not always required and there are very few products that have an impact on rumen fluke. |
Different flukicides will kill different stages of the fluke life cycle so it important to chose the correct product for the stage you are treating for. |
| Ectoparasites | The spread of mange and lice is caused by close contact between the animals, this is why ectoparasites spread more easily at the time of housing cattle. Because ectoparasites are spread so easily it is important to control an outbreak by not only treating cattle with obvious signs but all animals that have been in contact. | Ectoparasites can be controlled using synthetic pyrethroids or Macrocyclic Lactone (ML) Products |
Combination Products
Products that combine both a wormer and a flukicide can seem like an easy option when treating cattle but there are some important questions to ask before choosing a combination product
Do the cattle need to be treated for both worms and fluke?
Is the wormer appropriate for the stages of worms you are treating against?
Is the flukicide appropriate for the stages of fluke you are treating against?
The problem of wormer resistance when treating cattle is a growing problem not only in Ireland but in countries all around the world. Resistance is not always obvious at first but the results can be detrimental to your herd. Resistance is caused by the continuous use of the same group of wormer every year. A combination of tightly monitoring your herd and a strict dosing routine should reduce the risk of resistance on your farm.
Signs of resistance on your land
How to prevent resistance
Choosing the correct product for the parasites you are targeting is essential. This will give predictable results which will lessen the chances of having to retreat. This will in turn save time, money and reduce the chances of resistance on your farm. Below are some essential tips to ensure you are treating your livestock properly. Which ever product and method of administration you choose it is essential to always follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- Choose an appropriate product for the parasites you are targeting
- Make sure to store wormers appropriately, normally away from sunlight, away from extreme temperatures and sometimes in a fridge. All these details will be available on documents accompanying the wormers.
- Ensure all dosing equipment is clean, compatible with your choice of wormer and is measuring correctly.
- Dose according to liveweight to avoid under or over dosing
- Record everything properly. Product used, amount used, batch number, expiry date, animal id, treatment date and withdrawal periods
- Do not mix wormers together as this can cause the product to be inactive
Pour Ons
- Pour Ons should be applied down along the length of the flattest part of the animal's back
- Animals should not be treated when wet or if rain is expected, unless the product specifically says it is ok to do so
- Damaged skin should be avoided
- Areas contaminated with mud or manure should be avoided and cleaned before application
Injectables
- Clean and sterile equipment should always be used, if using the same syringe for multiple animals the needle should be disinfected between injections
- If the injection site is dirty it should be cleaned with an alcohol wipe before injecting
- Use an appropriate sized needle for the animal you are injecting
- Make sure the animal is appropriately restrained before injecting
- For subcutaneous injections raise a fold of skin and inject into the space created, as shown in the diagram below
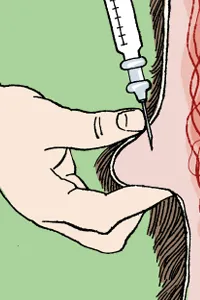
- Dispose of used needles and syringes in an appropriate sharps container
Oral Drenches
- Ensure all drenching equipment is clean and calibrated
- Ensure the animal is restrained with their head held up
- Slide the nozzle of the dosing gun into the side of the mouth and over the tongue so that the entire dose is swallowed immediately
Group 1: Benzimidazole (BZ) (White)
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | ||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Hornfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Albex 10% | Chanelle | Albendazole | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (Adult) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 14 Days | 60 Hours |
| Albex 2.5% | Channelle | Albendazole | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (Adult) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 14 Days | 60 Hours |
| Fenben 10 | Ancare | Fenbendazole | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 21 Days | X |
| Tramazole 10% | Univet | Albendazole | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (Adult) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 14 Days | 60 Hours |
Group 2: Levamisole (LV) (Yellow)
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | ||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Hornfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Levacide 7.5% Injection | Norbrook | Levamisole | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Injection SC | 28 Days | X |
Group 3: Macrocycli Lactones (ML) (Clear)
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | ||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Hormfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Animec 1% Injection | Chanelle | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Injection SC | 49 Days | X |
| Animec 0.5% Pour On | Chanelle | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Pour On | 49 Days | X |
| Cydectin 10% LA | Zoetis | Moxidectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Ear Injection | 108 Days | X |
| Dectomax Injection | Elanco | Doramectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Injection SC | 70 Days | X |
| Dectomax Pour On | Elanco | Doramectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Injection SC | 35 Days | X |
| Eprecis 20mg Injection | Ceva AH | Eprinomectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Injection SC | 63 Days | Zero |
| Eprinex Pour On | Boehringer | Eprinomectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Pour On | 15 Days | Zero |
| Eprizero Pour On | Norbrook | Eprinomectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Pour On | 10 Days | Zero |
| Imec 1% Injection | Acravet | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Injection SC | 49 Days | X |
| Imec Pour On | Acravet | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Pour On | 28 Days | X |
| Ivome Classic Pour On | Boehringer | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Pour On | 15 Days | X |
| Turbomec 1% Injection | Bimeda | Ivermectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Injection SC | 49 Days | X |
| Zeromectin | Chanelle | Eprinomectin | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Pour On | 28 Days | Zero |
Combination Products
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | ||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Hornfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Animec Super Injection | Chanelle | Ivermectin Clorsulon | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Injection SC | 66 Days | X |
| Bimectin Plus | Bimeda | Ivermectin Clorsulon | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Injection SC | 66 Days | X |
| Chan Broad Spec | Chanelle |
Rafoxanide Levamisole |
Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 60 Days | X |
| Closamectin Pour On | Norbrook | Ivermectin Clorsulon | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult and Immature over 7 weeks) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Pour On | 28 Days | X |
| Curafluke 10% | Univet | Rafoxanide Fenbendazole | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult and Immature) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 60 Days | X |
| Curafluke 5% | Univet | Rafoxanide Fenbendazole | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult and Immature) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 60 Days | X |
| Cydectin Triclamox | Zoetis | Moxidectin Triclabendazole | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult and immature) | No | No | Yes | No | No | Pour On | 143 Days | X |
| Ivomec Super Injection | Boehringer | Ivermectin Clorsulon | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Injection SC | 66 Days | X |
| Levafas Diamond | Norbrook | Levamisole Oxyclozanide | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 5 Days | X |
| Topimec Super Injection | Chanelle | Ivermectin Clorsulon | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Adult) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Injection SC | 66 Days | X |
Flukicides
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | ||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Hornfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Endofluke 10% | Bimeda | Triclabendazole | No | No | No | Yes (All Stages) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 56 Days | X |
| Fasinex 240 | Elanco | Triclabendazole | No | No | No | Yes (All Stages) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 56 Days | X |
| Flukiver Injection | Elanco | Closantel | No | No | No | Yes (Adult and Immature) | No | No | No | No | No | Injection SC | 77 Days | X |
| Rumenil | Chanelle | Oxyclozanide | No | No | Yes (Segments Only) | Yes (Adult only) | No | No | No | No | NO | Oral Drench | 28 Days | 72 Hours |
| Santiola Injection | KRKA | Closantel | No | NO | No | Yes (Adult and Immature) | No | No | No | No | No | Injection SC | 77 Day | X |
| Tribex 10% | Chanelle | Triclabendazole | No | No | No | Yes (All Stages) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 56 Days | X |
| Triclaben | Chanelle | Triclabendazole | No | No | No | Yes (All Stages) | No | No | No | No | No | Oral Drench | 56 Days | X |
| Trodax | Boehringer | Nitroxynil | No | No | No | Yes (Adult and Late Immature) | No | No | No | No | No | Injection sc | 60 Days | X |
Ectoparasiticides - Synthetic Pyrethroids
| Product | Company Name | Chemical Name | Parasites Controlled | Administration | Withdrawal (Meat) | Milk Withhold | |||||||||
| Roundworm | Lungworm | Tapeworm | Liver Fluke | Mites | Warbles | Lice | Flies | Hornfly | Eyeworm | ||||||
| Bayticol | Bayer | Flumethrin | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Pour On | 5 Days | 10 Days |
| Butox | MSD | Deltamethrin | No | No | Noj | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Pour On | 18 Days | 12 Hours |
| Ectospec | Bimeda | Cypermethrin | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Pour On | 10 Days | 12 Hours |
| Flectron Fly Tag | Zoetis | Cypermethrin | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Ear Tag | Zero | Zero |
| Spot On | Zoetis | Deltamethrin | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Spot On | 17 Days | Zero |
| Spotinor | Noorbrook | Deltamethrin | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Spot On | 17 Days | Zero |